Map of ancient greece pindus mountains – The map of ancient Greece: Pindus Mountains invites us on an extraordinary journey through time, revealing the captivating history, breathtaking landscapes, and enduring legacy of this iconic mountain range.
Nestled in the heart of Greece, the Pindus Mountains have stood as a formidable natural barrier, shaped countless civilizations, and harbored a wealth of cultural and ecological treasures.
Geography of the Pindus Mountains: Map Of Ancient Greece Pindus Mountains

The Pindus Mountains, also known as the Pindhos Mountains, form a prominent mountain range in mainland Greece, stretching from north to south. They constitute the central spine of the country, separating the regions of Epirus and Thessaly in western Greece from Macedonia and central Greece to the east.
The Pindus Mountains are known for their rugged terrain, high peaks, and deep gorges.
The Pindus Mountains extend for approximately 160 kilometers (100 miles) from Mount Grammos in the north to the Gulf of Corinth in the south. The highest peak in the range is Mount Smolikas, with an elevation of 2,637 meters (8,652 feet).
Other notable peaks include Mount Tymfi, Mount Giona, and Mount Vardousia.
Geologically, the Pindus Mountains are part of the Dinaric Alps, which extend from the Adriatic Sea to the Aegean Sea. The mountains were formed by the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates during the Alpine orogeny, which began around 30 million years ago.
The collision caused the Earth’s crust to fold and thrust upwards, creating the rugged landscape of the Pindus Mountains.
The Pindus Mountains are characterized by a complex geological structure, with a mix of sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks. The mountains are also home to numerous caves, gorges, and waterfalls, which have been formed by the erosive action of water and ice over millions of years.
A map of the Pindus Mountains can be found here: [link to map]
Historical Significance of the Pindus Mountains
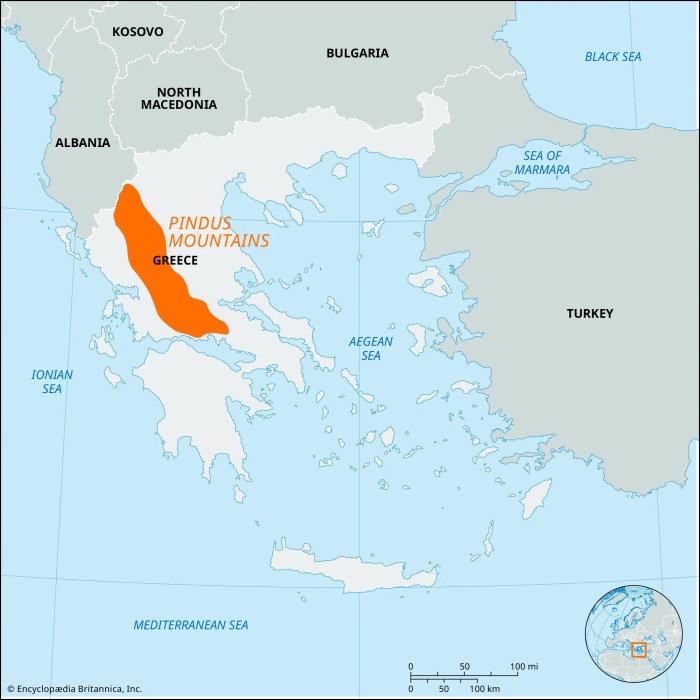
The Pindus Mountains have played a significant role in Greek history, serving as a natural barrier and a strategic military position.
In ancient times, the Pindus Mountains were home to the Perrhaebi, a Greek tribe that inhabited the region around Mount Olympus. The mountains also formed a natural boundary between the kingdoms of Epirus and Macedonia.
During the Greco-Persian Wars, the Pindus Mountains were the site of several important battles, including the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. In this battle, a small force of Greek soldiers led by King Leonidas of Sparta held off a much larger Persian army for three days, allowing the rest of the Greek army to retreat.
The Pindus Mountains also played a role in the Roman conquest of Greece. In 168 BC, the Roman general Lucius Aemilius Paullus defeated the Macedonian king Perseus at the Battle of Pydna, which took place in the foothills of the Pindus Mountains.
In the Middle Ages, the Pindus Mountains were a refuge for Greek Orthodox Christians who were fleeing from the Ottoman Turks. The mountains also became a center of resistance against Ottoman rule.
During the Greek War of Independence (1821-1829), the Pindus Mountains were the site of several important battles, including the Battle of Sarandapotamos in 1822. In this battle, a Greek force led by General Theodoros Kolokotronis defeated a larger Ottoman army.
The Pindus Mountains continue to be of strategic importance to Greece today. The mountains form a natural barrier between Greece and its northern neighbors, and they are home to several military bases.
Cultural and Archaeological Heritage of the Pindus Mountains
The Pindus Mountains are home to a rich cultural and archaeological heritage.
The mountains are home to several ancient settlements, including the ruins of the city of Dodona, which was once a major religious center in ancient Greece. The mountains are also home to several monasteries, churches, and other religious sites.
The Pindus Mountains have been inhabited since prehistoric times, and there are numerous archaeological sites in the region. These sites have yielded a wealth of artifacts, including pottery, tools, and weapons.
The Pindus Mountains are also home to a number of traditional villages and towns. These villages have preserved many of the traditional customs and practices of the region.
Ecological Significance of the Pindus Mountains
The Pindus Mountains are home to a diverse array of flora and fauna.
The mountains are home to several endemic species, including the Pindus fir, the Pindus jay, and the Balkan lynx. The mountains are also home to a number of protected areas, including the Pindus National Park.
The Pindus Mountains play an important role in the region’s water cycle. The mountains are home to several major rivers, including the Achelous, the Arachthos, and the Peneios. These rivers provide water for irrigation, drinking, and hydropower.
The Pindus Mountains are also home to a number of forests, which provide timber, fuel, and other resources. The forests also help to regulate the climate and protect the soil from erosion.
Tourism and Recreation in the Pindus Mountains
The Pindus Mountains are a popular destination for tourists and outdoor enthusiasts.
The mountains offer a variety of hiking trails, scenic drives, and cultural attractions. The Pindus National Park is a popular destination for hikers and nature lovers. The park is home to a variety of hiking trails, ranging from easy to challenging.
The Pindus Mountains are also home to several ski resorts. These resorts offer a variety of slopes for skiers and snowboarders of all levels.
The Pindus Mountains are a beautiful and diverse region that offers something for everyone. Whether you are looking for a challenging hike, a scenic drive, or a relaxing vacation, the Pindus Mountains are sure to have something to offer.
Question Bank
Where are the Pindus Mountains located?
The Pindus Mountains form the backbone of mainland Greece, stretching from the Albanian border in the northwest to the Gulf of Corinth in the south.
What is the highest peak in the Pindus Mountains?
Mount Smolikas, rising to an elevation of 2,637 meters (8,652 feet), is the highest peak in the Pindus Mountains.
What is the historical significance of the Pindus Mountains?
The Pindus Mountains have played a pivotal role in Greek history, serving as a natural barrier, a strategic military position, and a refuge for ancient civilizations.
What are some of the cultural attractions found in the Pindus Mountains?
The Pindus Mountains are home to numerous ancient settlements, monasteries, and traditional villages, offering a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of the region.
What are the main recreational activities available in the Pindus Mountains?
The Pindus Mountains offer a wide range of recreational activities, including hiking, mountain biking, skiing, and rafting, providing opportunities to explore the stunning landscapes and connect with nature.