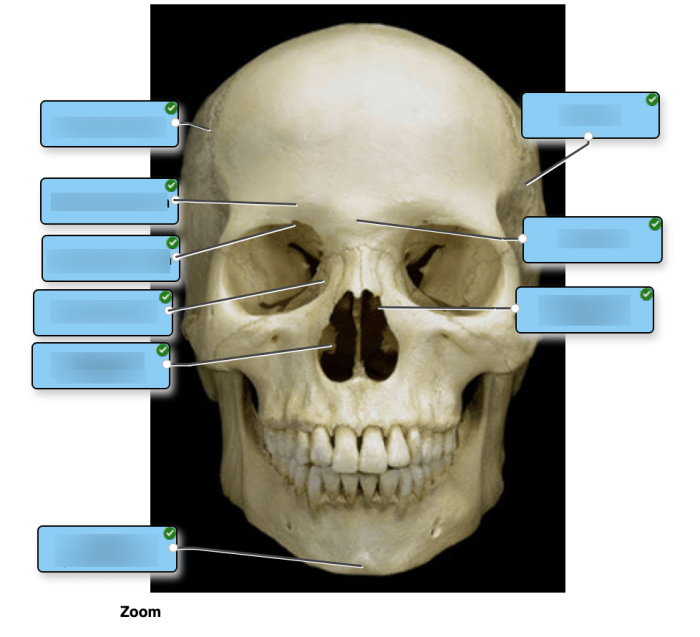
Label the specific bony features of the superior skull. – Embarking on an exploration of the intricate anatomy of the superior skull, this discourse delves into the specific bony features that define its structure and functionality. From the prominent frontal bone to the enigmatic ethmoid bone, each element plays a crucial role in shaping the skull’s protective and sensory functions.
Beginning with the frontal bone, we uncover its location and shape, examining the significance of the supraorbital margin and exploring the role of the frontal sinuses. The parietal bones, with their unique shape and position, form the sides of the skull, connected by the sagittal suture.
Their parietal foramina provide essential passageways for blood vessels and nerves.
Superior Skull: Bony Features
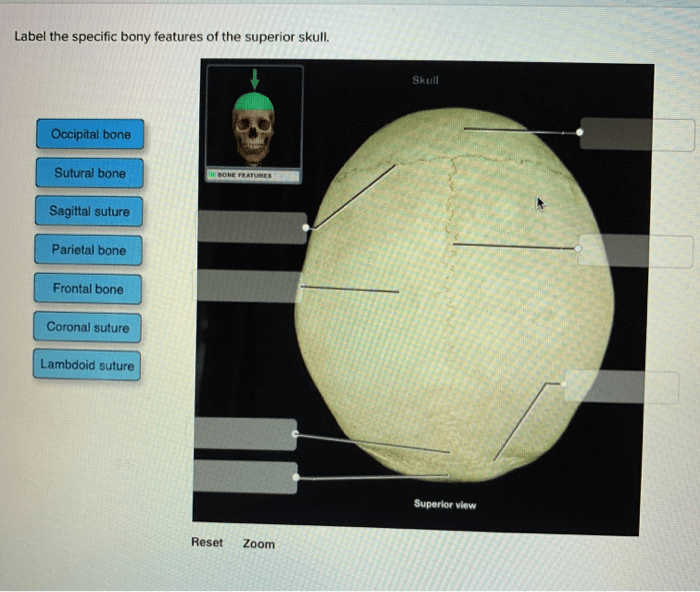
The superior skull, also known as the cranial vault, forms the roof and lateral walls of the skull. It consists of six paired bones: the frontal bone, two parietal bones, the occipital bone, two temporal bones, the sphenoid bone, and the ethmoid bone.
Frontal Bone
The frontal bone is located at the anterior aspect of the superior skull and forms the forehead and the roof of the orbits. It is shaped like a half-moon, with a convex outer surface and a concave inner surface. The frontal bone has several important features, including the supraorbital margin, the frontal sinuses, and the glabella.
- Supraorbital margin:The supraorbital margin is a prominent ridge that runs along the superior border of the orbit. It serves as an attachment site for the eyebrows and helps to protect the eyes from injury.
- Frontal sinuses:The frontal sinuses are air-filled cavities located within the frontal bone. They help to lighten the skull and resonate sound, which is important for speech and hearing.
- Glabella:The glabella is a small, smooth area located between the eyebrows. It is the most anterior point of the skull and is often used as a landmark for anatomical measurements.
Parietal Bones, Label the specific bony features of the superior skull.
The parietal bones are located on either side of the frontal bone and form the superior and lateral walls of the cranial vault. They are large, flat bones that are shaped like a quadrilateral. The parietal bones have several important features, including the sagittal suture, the parietal foramina, and the temporal lines.
- Sagittal suture:The sagittal suture is a fibrous joint that connects the two parietal bones along the midline of the skull. It is the longest suture in the skull and runs from the frontal bone to the occipital bone.
- Parietal foramina:The parietal foramina are small openings located on the inner surface of the parietal bones. They allow blood vessels and nerves to pass through the skull.
- Temporal lines:The temporal lines are two ridges that run along the lateral surface of the parietal bones. They serve as attachment sites for the temporalis muscle, which is responsible for chewing.
Occipital Bone
The occipital bone is located at the posterior aspect of the superior skull and forms the back and base of the cranial vault. It is a trapezoidal-shaped bone that has several important features, including the foramen magnum, the occipital condyles, and the nuchal crest.
- Foramen magnum:The foramen magnum is a large opening located at the base of the occipital bone. It allows the spinal cord to pass through the skull and connect to the brain.
- Occipital condyles:The occipital condyles are two oval-shaped projections located on either side of the foramen magnum. They articulate with the first cervical vertebra, the atlas, and allow the head to nod.
- Nuchal crest:The nuchal crest is a prominent ridge that runs along the posterior surface of the occipital bone. It serves as an attachment site for the muscles of the neck.
Common Queries: Label The Specific Bony Features Of The Superior Skull.
What is the function of the supraorbital margin?
The supraorbital margin forms the superior border of the orbit and provides attachment points for muscles involved in eyelid movement.
What is the significance of the sagittal suture?
The sagittal suture is a fibrous joint that connects the parietal bones and allows for growth of the skull during infancy.
What is the role of the foramen magnum?
The foramen magnum is a large opening in the occipital bone that allows for the passage of the spinal cord and vertebral arteries.